AFFINILUTE™ MIP - Triazine SPE sorbent for multi-residue extraction of triazines and triazine metabolites in water, soil and food products Triazines represent a class of
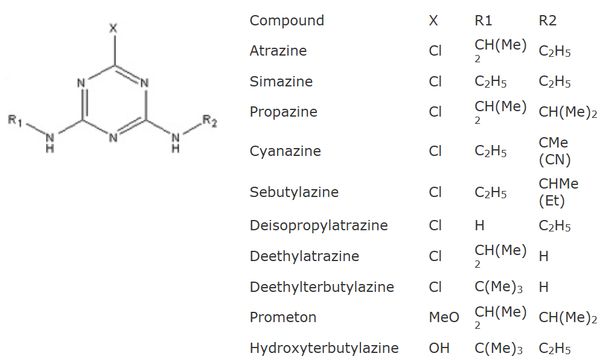
herbicides used in agricultural settings to control broadleaf weeds. Atrazine, simazine and propazine are three of the more commonly used triazines, having the general structure shown below. Despite their widespread use, triazines are known to be
harmful to animals and humans. Because of such health concerns herbicide use is
strictly regulated in the European Union. The use of triazines is
forbidden in most European countries. The European Legislation allows a maximum of 0.1 µg/L in drinking water. The US EPA has also set limits on the amounts of atrazine allowed in public drinking water supplies, food and animal feed. The ability to detect triazines is a global issue and a satisfactory analytical method for these compounds is in great demand.
The AFFINILUTE MIP - Triazine provides excellent selectivity for the following triazines and triazine metabolites: atrazine, simazine, propazine, cyanazine, sebutylazine, deisopropylatrazine, deethylatrazine, deethylterbutylazine, prometon and hydroxyterbutylazine. Extraction recoveries are reproducible and in the range 80-95%.
 Features and Applications
Features and ApplicationsAFFINILUTE MIP - Triazine allows for the robust extraction of triazines and triazine metabolites at low detection levels (ppb) from industrial wastewater, drinking and river water, in addition to food samples. AFFINILUTE MIP - Triazine is selective for the following triazines and triazine metabolites: atrazine, simazine, propazine, cyanazine, sebutylazine, deisopropylatrazine, deethylatrazine, deethylterbutylazine, prometon and hydroxyterbutylazine.
The analysis and extraction of triazines and triazine metabolites from water, with high recoveries even when present at very low levels (ppb), are characteristics of AFFINILUTE MIP - Triazine. The recoveries are reproducible and in the range 80-95%. Due to the selectivity of AFFINILUTE MIP - Triazine less ‘chemical noise’is apparent compared with conventional extraction methods, resulting in lower detection limits in GCMS or LCMS analysis. This also facilitates reduced sample volumes, quicker analysis times and a more cost effective extraction method.



